Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Partial Fill Holes#
This example fills all but the largest holes in a planar mesh using the lower level pymeshfix interface pymeshfix.PyTMesh.
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
from pymeshfix import PyTMesh
from pymeshfix import MeshFix
from pymeshfix import examples
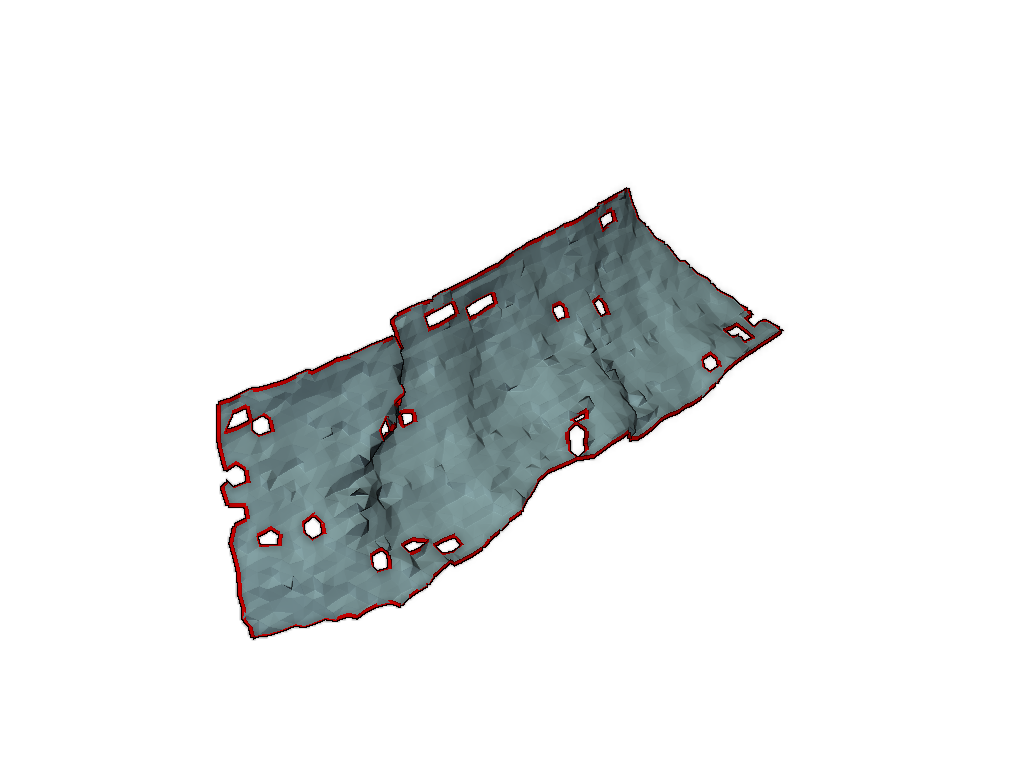
Plot the holes on the original mesh
orig_mesh = pv.read(examples.planar_mesh)
# orig_mesh.plot_boundaries()
meshfix = MeshFix(orig_mesh, verbose=True)
holes = meshfix.extract_holes()
# Render the mesh and outline the holes
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(orig_mesh, color=True, smooth_shading=True)
pl.add_mesh(holes, color="r", line_width=8, render_lines_as_tubes=True, lighting=False)
pl.enable_eye_dome_lighting() # helps depth perception
_ = pl.show()
This example uses the lower level C interface to the TMesh object.
mfix = PyTMesh()
mfix.set_quiet(True)
mfix.load_file(examples.planar_mesh)
# Fills all the holes having at at most 'nbe' boundary edges. If
# 'refine' is true, adds inner vertices to reproduce the sampling
# density of the surroundings. Returns number of holes patched. If
# 'nbe' is 0 (default), all the holes are patched.
mfix.fill_small_boundaries(nbe=100, refine=True)
16
Convert back to a pyvista mesh
vert, faces = mfix.return_arrays()
mesh = pv.make_tri_mesh(vert, faces)
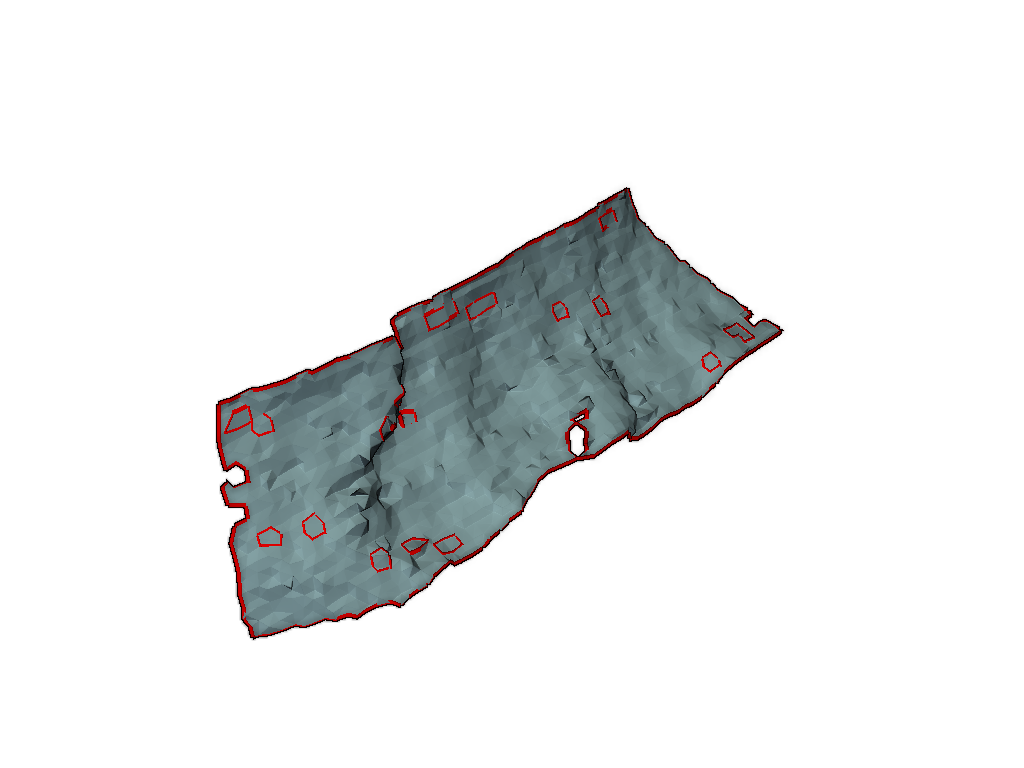
Plot the repaired mesh along with the original holes.
Note
It seems there is a limit to the repair algorithm whereby some of the holes that include only a single point are not filled. These boundary holes are not detected by VTK’s hole repair algorithm either.
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(mesh, color=True, smooth_shading=True)
pl.add_mesh(holes, color="r", line_width=8, render_lines_as_tubes=True, lighting=False)
pl.enable_eye_dome_lighting() # helps depth perception
_ = pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.788 seconds)
